Bandpass boxes have revolutionized how we experience deep and impactful bass in audio systems. These enclosures are ingeniously crafted to enhance and focus on specific sound spectrums, particularly the Bandpass Box Low Frequencies, essential for achieving that immersive, heart-thumping bass effect. For those keen on diving into the technicalities, understanding how these low frequencies are optimized within bandpass boxes can significantly elevate the performance of any sound system. This exploration is not just about the mechanics; it's about unlocking the potential of your audio setup to deliver unparalleled sound quality.
As we venture further into the intricacies of sound engineering, the role of Bandpass Box Low Frequencies becomes increasingly apparent. These frequencies are the backbone of a rich and dynamic audio experience, laying the foundation for what can be described as the soul of music and sound effects. Delving into the design and engineering aspects of bandpass boxes reveals how they are tailored to reproduce low frequencies and to do so with clarity and depth that transforms ordinary sound into extraordinary auditory landscapes. Whether you're crafting a system for professional use or personal enjoyment, the insights gained from understanding these low-frequency principles are invaluable for anyone looking to achieve excellence in audio reproduction.
Elevate Your Audio Experience: Get Your Bandpass Subwoofer Box Today!
Understanding Low Frequencies and Bandpass Boxes

Low frequencies, often associated with heart-pounding bass, are the foundation of a compelling sound system. These frequencies, typically ranging from 20Hz to 80Hz, are responsible for the depth, impact, and resonance of audio experiences. Bandpass boxes, also known as bandpass enclosures, provide a unique approach to harnessing low frequencies for optimal performance. By carefully tuning the enclosure design, bandpass boxes can amplify and isolate low frequencies, resulting in tight bass response and enhanced audio quality. To truly grasp the power of low frequencies in bandpass boxes, it's essential to understand the science behind sound waves, frequency ranges, and how these elements shape the audio experience.
The Science of Low Frequencies
When it comes to sound, everything starts with sound waves. Sound waves are vibrations that travel through a medium, such as air, and can be measured in frequency, amplitude, and wavelength. Frequency, which is the number of waves or cycles that occur in a given time, determines the pitch of a sound. Low frequencies, also called lower frequencies, have a longer wavelength and lower pitch than higher frequencies.
In the context of bandpass boxes, low frequencies typically range from 20Hz to 80Hz, although this range can vary depending on the specific audio system and design goals. These low frequencies create a deep bass response, adding richness and power to music and other audio content. The human ear is particularly sensitive to low frequencies, which is critical in delivering an immersive audio experience.
We must first consider the frequency response to understand low frequencies in bandpass boxes. Frequency response refers to the range of frequencies that an audio system can reproduce, and it is typically represented graphically in a frequency response curve. A flat frequency response, where all frequencies are reproduced accurately, is the ideal target for audio reproduction. However, achieving a flat frequency response, especially in the lower frequency range, can be challenging due to the physical limitations of speakers and enclosures.
Defining Bandpass Boxes
Bandpass boxes, also known as bandpass enclosures, are specialized enclosures designed to isolate and amplify specific frequency ranges, including low frequencies. Unlike sealed boxes, which provide tight and precise bass reproduction, bandpass boxes offer a unique approach to optimizing low-frequency performance.
A bandpass enclosure consists of two chambers: the front and rear chambers. These chambers work together to filter and amplify specific frequency ranges, allowing the bandpass box to deliver enhanced bass response. The front chamber, also known as the sealed chamber, isolates and dampens unwanted frequencies. In contrast, the rear chamber, the ported chamber, allows specific frequencies to pass through.
Sealed bandpass enclosures, as the name suggests, have a sealed front chamber and a ported rear chamber. This design provides a more controlled bass response with a narrower frequency range. On the other hand, ported bandpass enclosures have a ported front chamber and a rear chamber with a port. This design allows for a more comprehensive frequency range and increased sound output, making it suitable for applications where maximum bass response is desired.
Bandpass boxes, with their unique enclosure design, offer several advantages.
- They can provide greater sound output,
- improved efficiency
- enhanced bass response compared to sealed or ported boxes alone.
However, it's essential to understand the specific goals and requirements of the audio system before choosing a bandpass enclosure design. Factors such as the type of music, desired sound pressure levels, and available power handling will influence the appropriate bandpass box design selection.
In the following sections, we will explore the role of low frequencies in bandpass boxes, the impact of low frequencies on sound quality, and the design considerations that go into building exceptional bandpass boxes for optimal low-frequency performance. Join us as we dive into the intricacies of bass reproduction, frequency response, and the art of tuning bandpass enclosures.
What is a bandpass box, and how does it work for low frequencies?
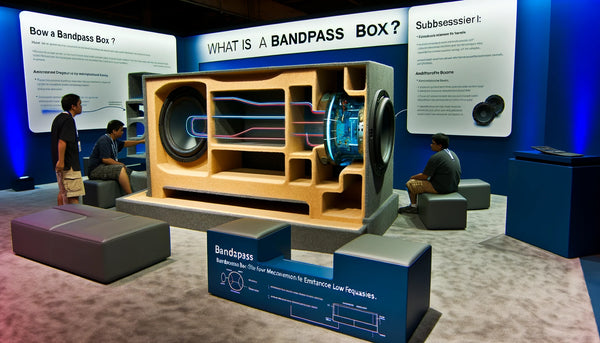
A bandpass box is an enclosure designed to enhance low-frequency sound reproduction performance. It works by filtering out unwanted frequencies and maximizing the output of targeted low frequencies, resulting in a more impactful and focused bass response.
The Role of Low Frequencies in Bandpass Boxes

The role of low frequencies in bandpass boxes is critical for achieving optimal bass reproduction and sound quality. These low frequencies, often associated with heart-pounding bass, create the immersive audio experience that audiophiles crave. Bandpass boxes can deliver tight bass response, improved transient response, and enhanced audio experience by carefully harnessing low frequencies. In the following sections, we will explore the impact of low frequencies on sound quality and how bandpass boxes can enhance bass sounds through lower frequencies.
Impact of Low Frequencies
The impact of low frequencies on sound quality cannot be overstated. The reproduction of low frequencies in bandpass boxes plays a crucial role in shaping the overall acoustic performance of sound systems. By carefully designing bandpass enclosures to optimize low-frequency response, audio enthusiasts and professionals can achieve a sound quality that is rich, immersive, and dynamic.
One of the primary benefits of low frequencies in bandpass boxes is the improved bass response. With their longer wavelengths, low frequencies are better suited for producing deep bass tones. By effectively reproducing low frequencies, bandpass boxes can deliver a bass response that is tight, controlled, and resonant. This, in turn, enhances the audio experience, allowing listeners to feel the music and immerse themselves in the sound.
Another aspect of sound quality influenced by low frequencies is the frequency response. The frequency response of an audio system refers to the range of frequencies that it can accurately reproduce. A flat frequency response, where all frequencies are reproduced with equal accuracy, is often desired for optimal sound quality. Low frequencies contribute to achieving this flat frequency response when reproducing accurately and in balance with the rest of the frequency range. This ensures the audio system faithfully reproduces the original sound without emphasizing or suppressing specific frequencies.
In addition to the bass and frequency responses, low frequencies also impact the transient response of audio systems. Transient response refers to the ability of an audio system to accurately reproduce short bursts of sound, such as the attack of a drum or the pluck of a guitar string. By providing tight and impactful low frequencies, bandpass boxes contribute to the transient response of the audio system, resulting in improved clarity, definition, and realism.
Ultimately, the impact of low frequencies on sound quality emphasizes the importance of bandpass box design in audio engineering. By carefully tuning the enclosure, optimizing the low-frequency response, and balancing the bass reproduction with the overall sound system, audio enthusiasts can achieve a sound quality that is immersive, dynamic, and true to the original recording. In the next section, we will explore how low frequencies, when harnessed effectively, can enhance bass sounds in bandpass boxes.
Enhancing Bass Sounds
Enhancing bass sounds in bandpass boxes involves harnessing lower frequencies to maximize the bass response's impact, depth, and clarity. By strategically incorporating lower frequencies, bandpass boxes can elevate the bass reproduction and create a rich, immersive audio experience.
One of how lower frequencies enhance bass sounds in bandpass boxes is through the bass reflex design. A bass reflex, also known as a ported design, utilizes a vent or port to improve the low-frequency response of the enclosure. The port works in conjunction with the rear chamber of the bandpass box, allowing air to flow in and out of the enclosure, extending the low-frequency response and improving the efficiency of bass reproduction. By optimizing the design of the port, including the length, diameter, and tuning frequency, audio enthusiasts can achieve a tight and powerful bass response.
Another method of enhancing bass sounds in bandpass boxes is using a low-pass filter. A low-pass filter is an electronic circuit that allows low frequencies to pass through while attenuating higher frequencies. By incorporating a low-pass filter into the bandpass box design, audio engineers can ensure that only the desired lower frequencies are reproduced, eliminating unwanted distortions or artifacts.
Furthermore, cone motion plays a crucial role in reproducing bass sounds. Lower frequencies, with their longer wavelengths, cause the speaker cone to move more substantially and more pronouncedly. Proper cone motion management, achieved through meticulous design and engineering, ensures that the speaker cone remains within its optimal range of motion, resulting in accurate, tight, and distortion-free bass reproduction.
Audio enthusiasts can optimize the bass reproduction in bandpass boxes by carefully considering the interplay of lower frequencies, bass-reflex design, low-pass filters, and cone motion. The result is a powerful, impactful, and tight bass response, enhancing the audio experience and immersing the listener in the music.
Designing Bandpass Boxes for Optimal Low Frequencies
Designing bandpass boxes for optimal low frequencies requires precise enclosure design, tuning frequency selection, and consideration of essential components. In the following sections, we will explore the crucial components of a low-frequency bandpass box and the different types of bandpass enclosures available for low-frequency reproduction. Join us as we dive into the design intricacies of bandpass boxes, unraveling the secrets behind achieving exceptional low-frequency performance.
Essential Components of a Low-Frequency Bandpass Box
It's important to understand the essential components contributing to its performance to design a bandpass box that optimizes low frequencies. These components include the enclosure design, tuning frequency, resonant frequency, and port area.
The enclosure design of a bandpass box plays a critical role in shaping the low-frequency system's low-frequency response. The enclosure's size, shape, and construction determine the resonant frequency, sound pressure levels, and overall bass reproduction. Different enclosure designs, such as single reflex, dual reflex, or hybrid designs, offer varying low-frequency performance, allowing audio enthusiasts to tailor the system to their specific needs.
Tuning frequency, also known as the resonant frequency, is another critical component in designing a bandpass box for optimal low frequencies. The tuning frequency determines the point at which the bandpass box resonates, amplifying specific frequencies within the low-frequency range. Audio enthusiasts can achieve the desired bass response and sound pressure levels by selecting the appropriate tuning frequency, delivering an immersive audio experience.
The port area of the bandpass box is another crucial element to consider. The port's size, length, and shape directly impact the efficiency of low-frequency reproduction and the overall bass response. Choosing the optimal port area ensures the bass reflex design is appropriately balanced, resulting in tight, controlled, and resonant bass reproduction.
Audio enthusiasts can design bandpass boxes that optimize low frequencies by carefully considering the enclosure design, tuning frequency, resonant frequency, and port area. These essential components form the foundation of exceptional bass reproduction, providing audio enthusiasts with the power, depth, and impact they desire. In the following sections, we will explore different types of bandpass boxes available for low frequencies, expanding the options for customized bass reproduction.
Different Types of Bandpass Boxes
Various bandpass boxes are available for low-frequency reproduction, each tailored to specific low-frequency ranges and design objectives. Exploring the different types of bandpass boxes sheds light on the diverse enclosure designs and ported chamber configurations.
One popular type of bandpass box design is the 4th-order bandpass box design. This design features a front and rear chamber, with the rear chamber vented through a port or vent. The 4th-order bandpass box design offers a narrower frequency range and increased sound output compared to sealed enclosures or 4th-order bandpass designs without the ported chamber. Audio enthusiasts can optimize the low-frequency response by carefully balancing the front and rear chamber volumes, achieving tight, impactful bass reproduction.
Another type of bandpass box design is the 6th-order bandpass box. The 6th-order bandpass box design utilizes multiple chambers and ports to achieve specific low-frequency performance. This design offers a limited bandwidth, allowing audio enthusiasts to focus on specific ranges of low frequencies. By carefully tuning the rear and front chamber volumes and port configurations, the 6th-order bandpass box design can deliver tight bass response, increased sound pressure levels, and enhanced transient response.
In addition to these specific designs, bandpass boxes can incorporate sealed and ported chambers in various configurations. Sealed chambers offer precise and controlled bass reproduction, while ported chambers enhance the low-frequency response and sound output. The combination of sealed and ported chambers allows for optimizing low frequencies, achieving a sound system that delivers the desired bass performance and audio experience.
By exploring the different types of bandpass boxes available for low frequencies, audio enthusiasts can expand their options for customized bass reproduction. Whether one chooses a 4th-order bandpass box design, a 6th-order bandpass box, or a combination of sealed and ported chambers, the goal is to achieve tight, resonant bass reproduction that immerses the listener in the music.
Tuning Bandpass Boxes to Lower Frequencies

To achieve optimal low frequency performance, tuning bandpass boxes is a critical step in the design process. The following sections will explore the importance of determining the desired frequency response and setting the tuning frequency for bandpass boxes. Join us as we unravel the complexities of tuning bandpass enclosures, allowing audio enthusiasts to unleash the full potential of low frequencies in their sound systems.
Determining the Desired Frequency Response
Determining the desired frequency response is crucial in tuning bandpass boxes for low frequencies. The frequency response refers to the range of frequencies that an audio system can accurately reproduce, and it plays a significant role in the overall sound quality.
Ideally, audio enthusiasts aim for a flat frequency response, where all frequencies, including low frequencies, are reproduced accurately without emphasis or suppression. Achieving flat frequency response requires careful design and tuning of the bandpass box, explicitly targeting the low-frequency range.
To determine the desired frequency response, audio enthusiasts analyze the specific goals of the sound system, the type of music or audio content being reproduced, and the listening preferences of the intended audience. By clearly defining the desired response, audio enthusiasts can tailor the bandpass box design, select the appropriate enclosure size, and optimize the low-frequency response for a resonant audio experience.
Specific enclosure designs also play a significant role in determining the frequency response of bandpass boxes. Different designs, such as single reflex, dual reflex, or hybrid designs, offer varying low-frequency performance, allowing audio enthusiasts to achieve specific sound signatures or cater to specific music genres.
Audio enthusiasts can tune bandpass boxes to deliver precise, accurate, and impactful low frequencies by carefully defining the desired frequency response and selecting the appropriate enclosure design. This ensures the sound system faithfully reproduces the music, taking the listener on an immersive audio journey.
Tuning Frequency for Optimal Low Frequencies
Setting the tuning frequency of a bandpass box is a critical step in achieving optimal low frequencies. The tuning frequency, also known as the resonant frequency, determines the frequency at which the bandpass box resonates, amplifying specific frequencies within the low-frequency range.
Audio enthusiasts consider various factors to set the tuning frequency, including the system's power handling, the vented chamber's design, and the port length. These elements directly impact the low-frequency bandpass box's response, sound pressure levels, and overall bass reproduction.
The power handling of the system influences the selection of the tuning frequency. It is crucial to ensure that the bandpass box can handle the power required to reproduce low frequencies accurately without distortion or damage. By selecting the tuning frequency with consideration of the power handling capabilities, audio enthusiasts can achieve bass reproduction that is tight, controlled, and resonant.
The design of the vented chamber, specifically the ported enclosure, also influences the tuning frequency. The port's size, length, and area contribute to the overall bass response, sound pressure levels, and efficiency of low-frequency reproduction. Audio enthusiasts can optimize the resonant frequency by tuning the vented chamber, ensuring the bandpass box delivers the desired bass performance.
Port length is critical in achieving the desired tuning frequency and low-frequency response. The port length affects the tuning frequency, sound pressure levels, and transient response of the bandpass box. Audio enthusiasts can fine-tune the low-frequency response by carefully calculating the port length, balancing deep bass reproduction and tight transient response.
Audio enthusiasts can optimize the low frequency performance of bandpass boxes by setting the tuning frequency considering power handling, vented chamber design, and port length. This ensures the bass reproduction is powerful, controlled, and resonant, providing listeners an immersive audio experience.
Overcoming Acoustic Challenges

Designing bandpass boxes for low frequencies has its fair share of acoustic challenges. In the following sections, we will explore the strategies for handling sound wave interference at lower frequencies and the solutions for impedance issues in bandpass boxes. Join us as we unravel the acoustic complexities of bandpass box design, equipping audio enthusiasts with the knowledge to overcome these challenges and achieve exceptional low-frequency performance.
Handling Sound Wave Interference
Sound wave interference challenges achieving optimal low-frequency performance in bandpass boxes. Sound waves, especially at lower frequencies, can interact with each other, leading to constructive or destructive interference and affecting the overall acoustic performance of the system.
Audio enthusiasts employ various strategies to handle sound wave interference at lower frequencies. One approach is to manage air pressure within the bandpass box carefully. Fluctuations in air pressure can cause sound waves to interfere, resulting in peaks and nulls in the frequency response. Audio enthusiasts can minimize air pressure issues by adequately balancing the rear chamber volumes, vented chamber design, and port configurations, ensuring consistent bass response across the frequency range.
Another strategy for handling sound wave interference is to address group delay. Group delay refers to the time it takes for different frequencies to pass through the bandpass box. When frequencies of a sound wave arrive at the listening area at different times, it can result in phase cancellations and inconsistencies in the bass reproduction. Audio enthusiasts can minimize group delay by carefully tuning the bandpass box, optimizing the ported enclosure design, and selecting appropriate enclosure sizes, achieving tight, synchronized bass reproduction.
By implementing these strategies, audio enthusiasts can overcome the acoustic challenges of sound wave interference at lower frequencies. The result is a bandpass box design that delivers accurate, controlled, and immersive bass reproduction, providing the listener with a resonant audio experience.
Solutions for Impedance Issues in Bandpass Boxes
Impedance issues pose another challenge in designing bandpass boxes for low frequencies. Impedance, measured in ohms, refers to the opposition of an audio system to the flow of electrical current. Variations in impedance, especially at specific frequencies, can significantly impact the power handling capabilities of the bandpass box, resulting in reduced sound quality and performance.
To address impedance issues in bandpass boxes, audio enthusiasts employ several solutions. One strategy is to design the bandpass box with impedance control in mind. Audio enthusiasts can optimize the impedance response by carefully considering the rear chamber volumes, front chamber volumes, and port configurations, ensuring stability and performance across the frequency range.
Additionally, power handling capabilities play a significant role in mitigating impedance challenges. Bandpass boxes, designed to handle specific power levels, should be selected or designed to match the power requirements of the audio system. Audio enthusiasts can minimize impedance issues by ensuring the bandpass box can handle the power required to reproduce low frequencies accurately, providing a robust and reliable bass reproduction.
By implementing these solutions, audio enthusiasts can overcome impedance issues in bandpass boxes, resulting in improved power handling, enhanced sound quality, and a smooth frequency response. These design considerations ensure that the bandpass box delivers the desired bass performance, immersing the listener in the music.
Practical Tips for Achieving Better Tuning Results

Achieving optimal tuning results in bandpass boxes requires careful attention to design and engineering. In the following sections, we will explore tips for mastering port design for low frequencies and how a well-tuned bandpass box enhances the audio experience. Join us as we unveil practical techniques that audio enthusiasts can incorporate to achieve their bandpass box designs' best possible tuning results.
Mastering Port Design for Low Frequencies
Port design plays a critical role in the performance of bandpass boxes, especially when it comes to low frequencies. The design of the port, including the size, length, and area, directly impacts the bandpass box's efficiency, response, and overall bass reproduction.
Mastering port design for low frequencies involves careful consideration of several factors. One such factor is the air pressure within the ported chamber. With the movement of the speaker cone, air pressure fluctuations occur within the enclosure. Audio enthusiasts can minimize air pressure issues by optimizing the port design, including the diameter, length, and area, ensuring consistent bass response and sound quality.
Another consideration in port design is port noise. Port noise, also known as chuffing, occurs when air turbulence disrupts the smooth flow of air through the port, resulting in unwanted noise or distortion. Carefully designing the port, ensuring an appropriate area, length, and shape, helps minimize port noise, delivering clean, distortion-free bass reproduction.
The port area is another crucial element in port design for low frequencies. The area of the port determines the bass reflex design's efficiency, impacting the bandpass box's sound pressure levels, bandwidth, and transient response. Audio enthusiasts can optimize the low-frequency performance by tuning the port area, ensuring tight, controlled, and resonant bass reproduction.
By mastering port design for low frequencies, audio enthusiasts can achieve bandpass box designs that deliver exceptional bass performance, impactful sound pressure levels, and an enhanced audio experience. These practical tips ensure the bandpass box delivers tight, resonant bass reproduction, immersing the listener in the music.
How a Well-Tuned Bandpass Box Enhances Audio Experience
A well-tuned bandpass box can significantly enhance the audio experience, creating a sound system that immerses the listener, delivering impactful sound pressure and precise transient response.
The quality of bass reproduction greatly influences the audio experience. A properly tuned bandpass box, optimized for low frequencies, ensures that bass response is tight, controlled, and resonant. This allows the listener to feel the music, experiencing low frequencies' full impact and power. Whether it's the heart-pounding bass of an action movie or the resounding thump of a bass guitar, a well-tuned bandpass box brings the audio experience to life.
Sound pressure levels are another crucial aspect of the audio experience. Audio enthusiasts can achieve sound pressure levels that command attention by carefully tuning the bandpass box and optimizing the resonant frequency, port design, and enclosure size. The bandpass box delivers the low frequencies with authority, filling the listening area with immersive bass reproduction.
The listening area experience is greatly enhanced through a well-tuned bandpass box. By carefully balancing the low-frequency response, transient response, and sound pressure levels, audio enthusiasts can create an audio system that offers consistent, enveloping bass reproduction throughout the listening area. Whether it's a small room, a home theater, or an ample event space, a well-tuned bandpass box ensures that every seat is the best seat in the house, providing an audio experience that captivates the listener.
Transient response, the ability of the bandpass box to accurately reproduce short bursts of sound, is also enhanced through proper tuning. By minimizing group delay, optimizing the ported chamber design, and fine-tuning the low-frequency response, audio enthusiasts can ensure that the bandpass box delivers tight, precise transients, improving clarity, definition, and realism.
A well-tuned bandpass box enhances the audio experience, bringing the music to life and immersing the listener in a world of resonant sounds. By paying attention to design, tuning, and acoustic performance, audio enthusiasts can unlock the full potential of low frequencies, creating sound systems that inspire, captivate, and engage the senses.
Advanced Concepts in Bandpass Box Design

Advanced low-frequency bandpass box design concepts allow audio enthusiasts and professionals to explore cutting-edge techniques for exceptional bass reproduction. In the following sections, we will dive into the intricacies of 4th-order bandpass enclosure variations and explore the principles behind 6th-order bandpass box design. Join us as we unravel the complexities of advanced bandpass box design, taking low-frequency performance to new heights.
Understanding 4th Order Bandpass Enclosure Variations
4th order bandpass enclosures, with their unique design, offer audio enthusiasts the opportunity to explore specific variations within the 4th-order bandpass box family. These variations, primarily focusing on the front and rear chamber volumes, provide different characteristics and performance capabilities.
The 4th-order bandpass enclosure design consists of a front and rear chamber, each serving a distinct purpose. The front chamber, also known as the sealed chamber, isolates and dampens, and the ported chamber allows specific frequencies to pass through.
Audio enthusiasts can achieve specific performance objectives by carefully balancing the volumes of the front and rear chambers. For example, increasing the front chamber volume can result in a narrower frequency range and tighter bass response. Decreasing the rear chamber volume, on the other hand, can lead to a broader frequency range and increased sound output.
Understanding the 4th-order bandpass enclosure variations allows audio enthusiasts to fine-tune the low-frequency performance of the bandpass box, achieving the desired sound signature or system requirements. Audio enthusiasts can tailor the bass response, sound pressure levels, and transient response by carefully adjusting the front and rear chamber volumes, delivering resonant bass reproduction that captivates the listener.
While the 4th-order bandpass enclosure offers specific advantages, it's essential to consider the specific design goals, power handling capabilities, and listening preferences when designing bandpass enclosures for low frequencies. The following section explores the 6th-order bandpass box design principles, expanding the options for advanced low-frequency performance.
Exploring 6th Order Bandpass Box Design
Exploring the design of a 6th-order bandpass box optimizes low frequencies, enhancing sound performance significantly. The specific enclosure designs attributed to the 6th-order bandpass box directly impact the reproduction of low frequencies, ensuring optimal sound quality. This design's limited bandwidth is crucial in achieving the desired sound performance. When constructing a 6th-order bandpass box, meticulous attention to acoustic performance is essential to achieve the desired results. It's worth noting that the rear chamber and front chamber volumes of the 6th-order bandpass box design can significantly impact the low-frequency response, necessitating precise calculations and measurements for an authoritative yet approachable outcome.
Building Your Own Low-Frequency Bandpass Box

Building your low-frequency bandpass box involves considering the size of the port and the cubic foot volume of the front and vented chamber. Choosing between the sealed and vented chamber is essential, considering the loudspeaker design and the type of music you prefer. A smaller enclosure might be suitable for home theater setups, while a larger one with a single reflex design may be preferable for higher db SPL. In the market today, you can find various band pass enclosures like the sealed box or ported box, such as those by JL Audio, which can significantly impact the sound quality based on the speaker cone and front and rear chamber volumes. Mastering the construction methodologies is crucial, along with precautions to ensure optimal sound while building your custom low-frequency bandpass box.
Construction Methodologies for Optimal Sound
Precise tuning frequency and port length calculations are essential to achieve optimal sound in bandpass boxes. Construction methodologies focusing on air pressure and cone motion contribute to tight bass reproduction. During construction, it's crucial to consider the bandpass box design's resonant frequency for a flat response. Attention to ported chamber design plays a significant role in achieving specific sound pressure levels. Additionally, acoustic performance relies on implementing appropriate techniques for managing port noise. By carefully addressing these construction methodologies, bandpass boxes can deliver the desired tight bass and optimal sound.
Precautions to Consider While Constructing Bandpass Boxes
When constructing bandpass boxes, taking precautions is vital to prevent group delays in sound waves. Attention to the type of enclosure design is crucial to avoid heart attack frequencies. Additionally, considering the size of the port impacts the bass response in the listening area. It's imperative to avoid rear chamber air pressure issues to maintain sound quality. Applying appropriate enclosure design principles is crucial to prevent limited bandwidth in bandpass boxes. The bandpass box can deliver optimal performance and ensure a seamless audio experience by carefully considering these precautions during construction.
How Does the Type of Bandpass Box Impact the Sound Quality?

The sound quality of a bandpass box is directly influenced by its type. Different types of bandpass boxes can impact bass reproduction, transient response, frequency range, power handling, and sound pressure levels. Understanding the type of bandpass box is crucial for optimizing enclosure size and achieving a desired flat frequency response and bass reflex.
Conclusion

To truly appreciate and enjoy music's deep bass sounds, it is essential to understand the role of low frequencies in bandpass boxes. These specialized enclosures are designed to enhance the lower frequencies, resulting in a more immersive audio experience. Bandpass boxes can deliver powerful and precise bass tones by manipulating the sound waves and overcoming acoustic challenges.
However, designing and tuning a bandpass box for optimal low frequencies requires careful consideration and expertise. Every aspect is crucial in achieving the desired frequency response, from selecting the right components to mastering port design. It is also essential to avoid common mistakes that can negatively impact the sound quality.
Building your low-frequency bandpass box can be rewarding whether you are a DIY enthusiast or an audio professional. Follow construction methodologies and take necessary precautions to ensure sound performance.
In conclusion, understanding and harnessing the power of low frequencies in bandpass boxes can elevate your audio experience to new heights. So dive into the world of low-frequency sound reproduction and unlock the full potential of your music.





